In today’s fast-paced digital age, the way we handle money and conduct transactions has undergone a significant transformation. One of the most notable shifts in recent years is the rise of mobile wallets. These digital tools, often just a tap away on our smartphones, promise a future where physical cash might become obsolete. But what exactly are mobile wallets, and why have they become such an integral part of our daily lives?
What is a Mobile Wallet?
A mobile wallet, at its core, is a digital version of the physical wallet you carry in your pocket. It stores payment card information, digital cash, and sometimes even loyalty cards and tickets. Instead of fumbling through a purse or wallet to find a credit card or cash, users can pay for goods and services by simply using their smartphones.
| Mobile Wallet | Country of Origin | Notable Features |
|---|---|---|
| Apple Pay | USA | NFC technology, Integration with Apple products |
| Google Wallet | USA | Peer-to-peer payments, Integration with Google services |
| Samsung Wallet | South Korea | Magnetic Secure Transmission, NFC technology |
| Alipay | China | QR code payments, Integration with Alibaba |
| Paytm | India | Mobile recharge, Bill payments |
Evolution of Mobile Payments
The journey of mobile payments is a fascinating tale of innovation, adaptation, and global acceptance. While today we might take the convenience of mobile wallets for granted, their evolution is deeply rooted in technological advancements and changing consumer behaviors.
The Early Days: Japan Leads the Way
The inception of mobile payments can be traced back to the early 2000s in Japan. NTT DoCoMo, a prominent Japanese mobile phone operator, introduced a mobile payment service called “i-mode” which allowed users to make purchases through their mobile phones. This was a revolutionary concept at the time and marked the beginning of a new era in digital payments.
The Rise of NFC Technology
Near Field Communication (NFC) technology played a pivotal role in the evolution of mobile payments. NFC allows two devices to communicate when they’re brought close together, making it perfect for secure, contactless transactions. The introduction of NFC chips in smartphones paved the way for mobile wallets like Apple Pay and Google Wallet, which rely on this technology for their tap-and-pay features.
Global Acceptance and Diverse Platforms
As smartphones became ubiquitous, the idea of mobile payments started gaining traction worldwide. Different regions saw the emergence of their own mobile payment platforms tailored to local needs. For instance, in Africa, M-Pesa became a popular mobile money transfer service, while in China, Alipay and WeChat Pay dominated the market.
| Year | Notable Developments |
|---|---|
| 2004 | Launch of i-mode in Japan |
| 2011 | Introduction of Google Wallet |
| 2014 | Apple Pay enters the market |
| 2016 | Samsung Pay’s global expansion |
| 2018 | Over 2 billion mobile wallet users worldwide |
The Concept of Mobile Wallets
To truly appreciate the impact of mobile wallets, it’s essential to understand their underlying mechanics and functionalities. These digital tools are more than just a replacement for physical wallets; they represent a convergence of technology, finance, and consumer behavior.
Defining Mobile Wallets
A mobile wallet is a digital tool that allows users to store payment information and other financial details securely on their mobile devices. This encompasses credit and debit card details, bank account information, loyalty cards, and even digital currencies. The primary objective is to facilitate electronic transactions without the need for physical cards or cash.
How Do Mobile Wallets Work?
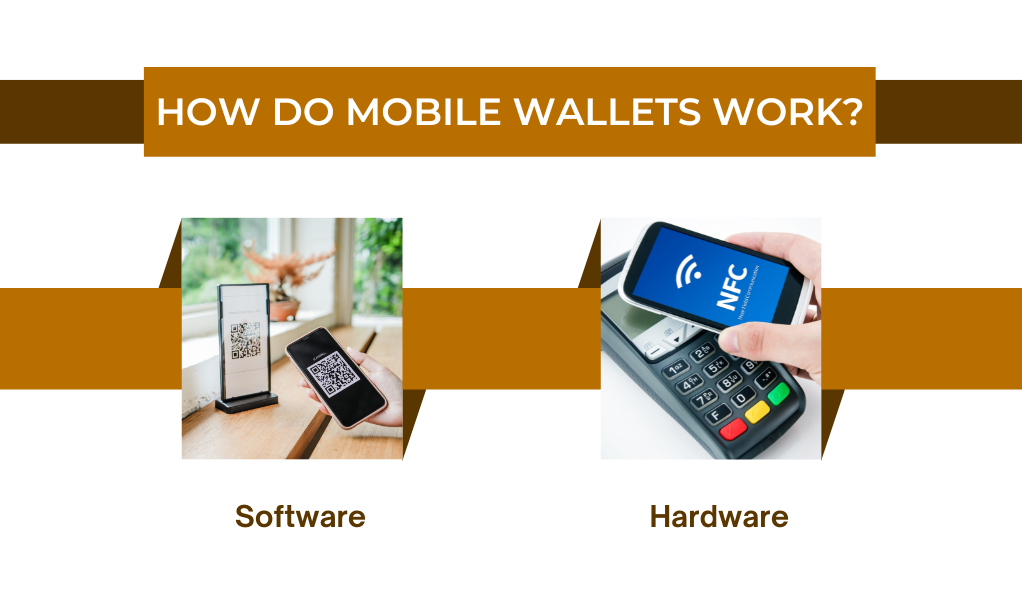
The operation of a mobile wallet is a blend of software and hardware:
- Software: Mobile wallets are typically offered as apps that users can download on their smartphones. These apps are secured with passwords, biometrics, or other authentication methods.
- Hardware: Modern smartphones come equipped with NFC chips that enable contactless payments. When a user makes a payment, the mobile wallet communicates with the Point of Sale (POS) terminal using NFC, facilitating a seamless transaction.
Types of Mobile Wallets
There are primarily three types of mobile wallets, each serving a distinct purpose:
- Closed Wallets: Offered by specific service providers, they can only be used for the services of that particular provider. For instance, the Amazon Pay balance can only be used on Amazon’s platform.
- Semi-closed Wallets: These wallets can be used to transact with multiple merchants but don’t permit cash withdrawals or redemptions. Paytm, without its banking features, is an example.
- Open Wallets: These are like digital bank accounts. Users can make purchases, transfer funds, and even withdraw cash. Examples include wallets offered by banks or financial institutions.
Benefits of Mobile Wallets
- Speed: Transactions are quicker compared to traditional methods.
- Convenience: No need to carry physical cash or cards.
- Offers and Rewards: Many mobile wallets offer discounts, cashbacks, and loyalty points.
- Integration: They can be integrated with other apps and services for a unified experience.
Convenience of Mobile Wallets
The meteoric rise of mobile wallets can be attributed largely to the unparalleled convenience they offer. In this section, we’ll delve into the various facets of this convenience, highlighting why mobile wallets have become an indispensable tool for many.
Ease of Use
One of the primary reasons for the popularity of mobile wallets is their user-friendly nature. Setting up a mobile wallet is typically a straightforward process:
- Download the App: Most mobile wallets are available as apps on major app stores.
- Registration: Users need to sign up, usually with their phone numbers or email addresses.
- Link Payment Methods: Add bank accounts, credit/debit cards, or load money into the wallet.
Once set up, making payments is as simple as selecting the payment method and authenticating the transaction.
Seamless Transactions
Gone are the days of writing checks or counting exact change. With mobile wallets:
- Tap and Pay: For in-store purchases, users can simply tap their phones on NFC-enabled POS terminals.
- Scan and Pay: Many wallets offer QR code-based payments, where users scan a code to complete transactions.
- Online Shopping: Mobile wallets can be used for e-commerce checkouts, streamlining the payment process.
Integration with Other Services
Mobile wallets aren’t just for payments. Their true potential shines when integrated with other services:
- Bill Payments: Utilities, credit card bills, and even rent can be paid using mobile wallets.
- Ticket Booking: Integration with entertainment and travel platforms allows users to book tickets seamlessly.
- Food and Delivery: Order food, groceries, or other essentials directly through the wallet app.
Security Concerns
While mobile wallets offer unparalleled convenience, they also introduce a set of security concerns. As digital platforms storing sensitive financial information, they become attractive targets for cybercriminals. Let’s delve into the potential risks associated with mobile wallets and real-world instances that highlight these concerns.
Potential Risks
- Unauthorized Access: If someone gains access to a user’s phone and the wallet app isn’t adequately protected, unauthorized transactions could occur.
- Phishing Attacks: Cybercriminals might trick users into revealing their mobile wallet credentials through fake emails or messages.
- Malware and Spyware: Malicious software can be installed on a user’s device, which could then capture sensitive information.
- Data Breaches: Mobile wallet providers store user data on servers. If these servers are compromised, user data could be at risk.
- Transaction Errors: Technical glitches could lead to incorrect transactions, where users might be charged incorrectly.
Real-World Instances
- 2016: Major Mobile Wallet Breach: A popular mobile wallet reported a security breach where unauthorized transactions were made from user accounts. The company had to refund the affected users and enhance its security measures.
- Phishing Scams: There have been numerous instances where users received fake messages claiming to be from their mobile wallet provider, asking them to click on a link or download an app, leading to data theft.
- Unsecured Wi-Fi Networks: Users accessing their mobile wallets on public Wi-Fi networks have sometimes fallen prey to ‘Man-in-the-Middle’ attacks, where cybercriminals intercept and alter communications between two parties.
Measures to Enhance Security

The concerns surrounding the security of mobile wallets have led to significant advancements in protective measures. Both wallet providers and financial institutions are continuously working to ensure that user data and funds remain safe. In this section, we’ll explore the various technologies and practices in place to fortify mobile wallet security.
Tokenization: The Shield of Mobile Payments
One of the primary security measures employed by mobile wallets is tokenization. Instead of transmitting actual card details during a transaction, a unique token is generated and sent. This token is useless if intercepted, as it doesn’t contain the actual card details.
Biometric Authentication: Personal and Unique
Modern smartphones come equipped with fingerprint scanners, facial recognition, and even iris scanners. Mobile wallets leverage these features, allowing users to authenticate transactions using their unique biometric data, adding an extra layer of security.
Encryption: Scrambling Data
All data stored and transmitted by mobile wallets is encrypted. This means that even if a hacker intercepts the data, they would only see a scrambled version of it, making it nearly impossible to decipher the actual information.
Secure Element: A Safe Storage
Some mobile wallets store sensitive data in a secure element (SE) – a tamper-resistant platform capable of securely hosting applications. The SE ensures that even if a phone is compromised, the data within the SE remains inaccessible.
Regular Security Audits
Reputable mobile wallet providers regularly undergo security audits. These audits, conducted by third-party organizations, ensure that the wallet’s security measures are up-to-date and can effectively counter current threats.
User Education and Awareness
Many security breaches occur due to user negligence. Wallet providers often run awareness campaigns, educating users about potential threats and how to avoid them. Simple measures, like not sharing PINs or passwords and being wary of phishing attempts, can go a long way in ensuring security.
Collaboration with Financial Institutions
Banks and credit card companies have a vested interest in the security of mobile payments. They often collaborate with wallet providers, sharing knowledge, and resources to enhance security measures.
Conclusion
As we stand on the cusp of a digital revolution, mobile wallets epitomize the fusion of technology, finance, and consumer convenience. From their humble beginnings to their current status as global financial tools, they have transformed the way we transact, offering speed, efficiency, and a touch of modernity to our daily financial interactions.
However, like all innovations, they come with their set of challenges. Balancing convenience with security remains a pivotal concern, but as we’ve seen, continuous advancements are being made to ensure users can transact with confidence. Collaboration between tech giants, financial institutions, and cybersecurity experts is fostering an environment where safety and ease coexist.




