The financial landscape has undergone a radical transformation in the last decade, with the advent of cryptocurrency challenging the long-established norms of traditional banking. As we delve into this comparative analysis, it is crucial to understand that both cryptocurrency and traditional banking have their unique strengths and weaknesses, and they cater to different needs and preferences.
The Rise of Digital Currencies
Cryptocurrency, a digital or virtual form of currency, has gained significant traction since the introduction of Bitcoin in 2009. It operates on decentralized networks based on blockchain technology—a distributed ledger that ensures transparency and security. The allure of cryptocurrency lies in its ability to facilitate fast and secure transactions without the need for intermediaries, such as banks or financial institutions.
The Persistence of Traditional Banking
On the other hand, traditional banking has been the backbone of our financial system for centuries. Banks provide a wide array of services, including savings and checking accounts, loans, mortgages, and investment products. They operate under stringent regulatory frameworks, ensuring stability and protecting consumer interests. Despite the rise of digital alternatives, traditional banks continue to play a vital role in the economy, offering reliability and a sense of security that digital currencies are yet to match fully.
Setting the Stage for Comparative Analysis
As we embark on this journey to compare and contrast cryptocurrency and traditional banking, it is important to acknowledge that this is not a black-and-white scenario. Both systems coexist, each serving different purposes and audiences. The following sections of this article will delve deeper into the intricacies of cryptocurrency and traditional banking, providing a comprehensive analysis to help you understand their respective roles in the modern financial landscape.
Understanding Cryptocurrency
Cryptocurrency represents a paradigm shift in how we perceive and interact with money. It is a digital or virtual currency that uses cryptography for security, making it extremely difficult to counterfeit or double-spend. Here, we delve into the core aspects of cryptocurrency to provide a comprehensive understanding.
What is Cryptocurrency?
At its core, cryptocurrency is a decentralized digital asset. Unlike traditional currencies issued by governments (fiat currencies), cryptocurrencies operate on technology called blockchain. A blockchain is a distributed ledger that records all transactions made with cryptocurrencies, ensuring transparency and security.
How Does it Work?
Cryptocurrencies leverage blockchain technology to gain decentralization, transparency, and immutability.
- Decentralization: Unlike centralized banking systems, most cryptocurrencies are decentralized and run on a technology called blockchain. A network of computers (nodes) collectively manages the database that records all transactions.
- Cryptography: Security in cryptocurrencies is maintained through cryptographic techniques. Each user has a public key (an address that others can see and send funds to) and a private key (known only to the owner, used to sign transactions and access funds).
- Mining: This is the process by which new cryptocurrency coins or tokens are created and added to the blockchain. It involves solving complex mathematical problems that validate and secure transactions on the network.
Key Features of Cryptocurrency
- Anonymity: Cryptocurrencies provide a level of anonymity for users. While the transaction details are stored in the blockchain, the identities of the people involved in transactions are encrypted.
- Speed and Accessibility: Transactions made with cryptocurrencies are processed quickly, regardless of the location of the parties involved. Additionally, cryptocurrencies are accessible to anyone with an internet connection, providing financial services to those without access to traditional banking.
- Volatility: Cryptocurrencies are known for their price volatility. The value of a cryptocurrency can skyrocket one day and plummet the next.
Popular Cryptocurrencies
- Bitcoin (BTC): The first and most well-known cryptocurrency.
- Ethereum (ETH): Known for its smart contract functionality.
- Ripple (XRP): Popular for its digital payment protocol more than its cryptocurrency.
- Litecoin (LTC): Created as the “silver to Bitcoin’s gold”.
Cryptocurrencies represent a revolutionary approach to money, offering a decentralized and digital alternative to traditional fiat currencies. While they have their advantages, such as speed and anonymity, they also come with risks and challenges, including volatility and security concerns. The next section will provide a similar deep dive into traditional banking, setting the stage for a comprehensive comparative analysis.
Understanding Traditional Banking
Traditional banking has been the cornerstone of financial systems worldwide, providing stability, security, and a wide range of services to individuals and businesses alike. In this section, we will explore the fundamental aspects of traditional banking to offer a clear and comprehensive understanding.
What is Traditional Banking?
Traditional banking refers to the financial services provided by established banking institutions that operate within a regulated framework. These services include, but are not limited to, accepting deposits, providing loans, offering investment products, and facilitating payments and transactions.
How Does it Work?
Traditional banks operate under a well-defined structure, adhering to stringent regulatory standards to ensure stability and protect consumer interests.
- Accepting Deposits: Customers deposit money into various types of accounts, such as savings, checking, or fixed deposits. The bank safeguards these deposits and pays interest on them.
- Providing Loans: Banks lend money to individuals, businesses, and governments, earning interest on the borrowed amount. This is a primary source of revenue for banks.
- Payment and Transaction Services: Banks offer a range of services to facilitate payments and transactions, including credit and debit cards, wire transfers, and online banking.
- Investment Services: Many banks provide investment services, helping customers grow their wealth through various financial instruments.
Key Features of Traditional Banking
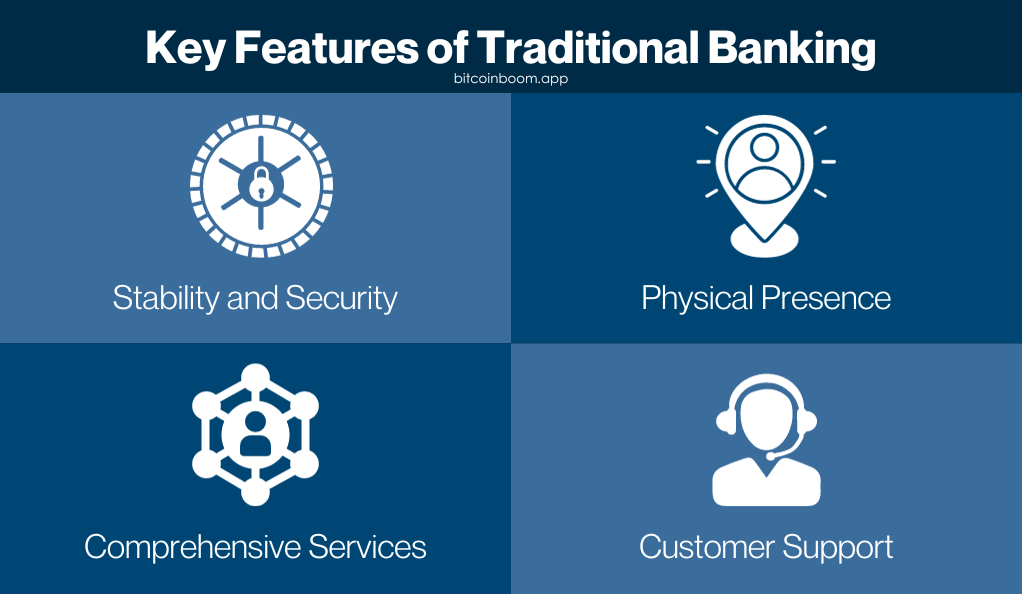
- Stability and Security: Traditional banks are known for their stability and security, with rigorous regulatory oversight ensuring that customer deposits are safe.
- Physical Presence: Unlike cryptocurrencies, traditional banks have a physical presence, with branches and ATMs providing accessibility to customers.
- Comprehensive Services: Banks offer a comprehensive range of financial services under one roof, catering to the diverse needs of their customers.
- Customer Support: Traditional banks provide extensive customer support, with personnel available to assist customers with their financial needs and queries.
Challenges and Criticisms
- Bureaucracy and Inefficiency: Traditional banking systems can be bureaucratic, with lengthy processes for loan approvals and other services.
- Limited Accessibility: While banks have a wide reach, there are still regions, particularly in developing countries, where access to banking services is limited.
- Fees and Charges: Customers often face various fees and charges for banking services, which can be a point of contention.
Traditional banking has played a pivotal role in shaping the financial world as we know it today. It offers stability, security, and a wide array of services to cater to the diverse needs of the population. However, it is not without its challenges, and the rise of digital alternatives like cryptocurrency is prompting traditional banks to evolve and adapt. The next sections will delve into a comparative analysis, highlighting the pros and cons of each system and their impact on the global economy.
Comparative Analysis: Pros and Cons
In this section, we will delve into a comprehensive comparison between cryptocurrency and traditional banking, highlighting the advantages and disadvantages of each to provide a balanced perspective.
Advantages of Cryptocurrency over Traditional Banking
- Decentralization: Cryptocurrencies operate on decentralized networks, reducing the need for intermediaries and potentially lowering transaction costs.
- Speed: Cryptocurrency transactions, especially cross-border ones, can be completed more quickly than traditional bank transactions.
- Accessibility: Cryptocurrencies are accessible to anyone with an internet connection, providing financial services to unbanked and underbanked populations.
- Innovation: The blockchain technology underlying cryptocurrencies has paved the way for innovative financial products and services.
Advantages of Traditional Banking over Cryptocurrency
- Stability: Traditional banks offer a stable and secure environment for customers to deposit their money, backed by government insurance in many cases.
- Comprehensive Services: Banks provide a wide range of financial services, from loans and mortgages to investment and insurance products, all under one roof.
- Customer Support: Traditional banks offer extensive customer support, with personnel available to assist customers in various capacities.
- Regulation: Banks operate under stringent regulatory frameworks, ensuring transparency, accountability, and consumer protection.
Disadvantages and Risks Associated with Both
| Aspect | Cryptocurrency | Traditional Banking |
|---|---|---|
| Security | Vulnerable to hacks and cyber-attacks. Loss of private key can result in loss of funds. | Generally secure, but still susceptible to fraud and cyber-attacks. |
| Volatility | Highly volatile, with prices subject to rapid fluctuations. | Stable, with government-backed insurance providing an additional safety net. |
| Regulation | Lack of clear regulatory frameworks in many regions, leading to uncertainty. | Stringent regulations can sometimes result in bureaucratic processes. |
| Accessibility | Requires internet access, potentially excluding certain populations. | Physical branches provide widespread accessibility, but may be limited in remote areas. |
| Transaction Speed | Fast, especially for cross-border transactions. | Can be slow, particularly for international transfers. |
| Innovation | Constantly evolving, with new products and services frequently introduced. | Traditionally slower to innovate due to regulatory constraints and legacy systems. |
Both cryptocurrency and traditional banking have their unique advantages and disadvantages, catering to different needs and preferences. Cryptocurrency offers speed, innovation, and accessibility, challenging the traditional financial systems and prompting change. On the other hand, traditional banking provides stability, comprehensive services, and extensive customer support, continuing to play a vital role in the global economy.
Security and Regulation
In the financial world, security and regulation play pivotal roles in ensuring the stability of systems and the protection of consumers. This section explores how these aspects are handled in both cryptocurrency and traditional banking.
Security in Cryptocurrency
Cryptocurrencies leverage advanced cryptographic techniques to secure transactions and control the creation of new units. However, they are not without their vulnerabilities.
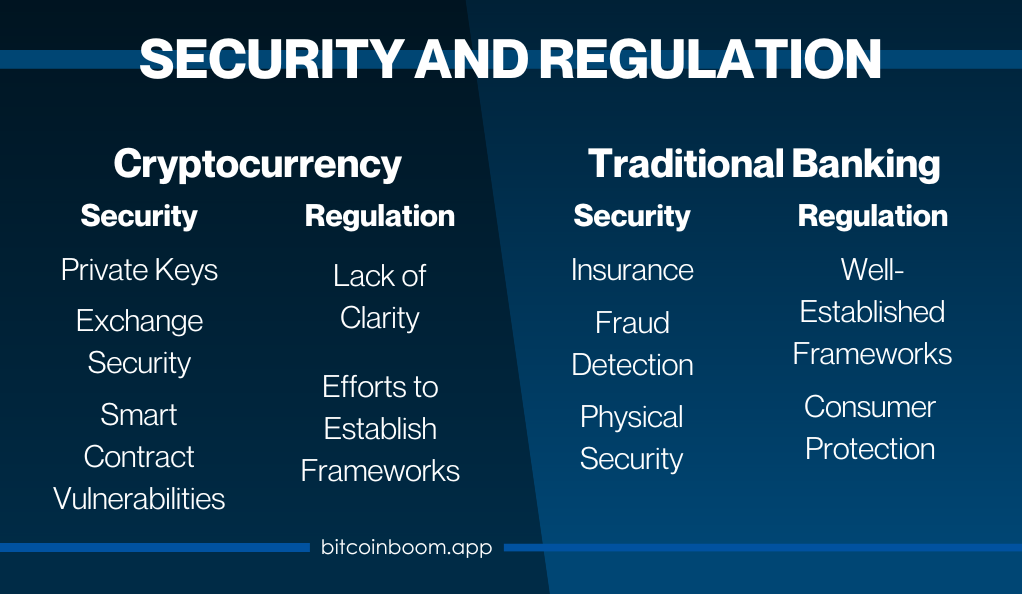
- Private Keys: Users must secure their private keys. Losing access to a private key means losing access to the funds.
- Exchange Security: Cryptocurrency exchanges are common targets for hackers. Users need to be cautious and use exchanges with robust security measures.
- Smart Contract Vulnerabilities: Cryptocurrencies like Ethereum use smart contracts, which can have vulnerabilities if not properly audited.
Security in Traditional Banking
Traditional banks have developed comprehensive security measures to protect customer funds and personal information.
- Insurance: Many countries offer deposit insurance, protecting customer deposits up to a certain amount.
- Fraud Detection: Banks employ advanced fraud detection systems to monitor transactions and prevent unauthorized access.
- Physical Security: Banks’ physical presence adds an additional layer of security, with secure vaults for storing cash and valuable items.
Regulatory Landscape
The regulatory landscape for cryptocurrency and traditional banking varies significantly, reflecting their different natures and maturity levels.
Cryptocurrency Regulation
- Lack of Clarity: The regulatory environment for cryptocurrencies is still evolving, with a lack of clarity in many regions.
- Efforts to Establish Frameworks: Governments and regulatory bodies are working to establish clear frameworks to prevent illegal activities and protect consumers.
Traditional Banking Regulation
- Well-Established Frameworks: Traditional banks operate under well-established regulatory frameworks, ensuring transparency and accountability.
- Consumer Protection: Regulations are in place to protect consumers, including deposit insurance and dispute resolution mechanisms.
Challenges and Ongoing Developments
The financial world is constantly evolving, and both cryptocurrency and traditional banking face ongoing challenges in terms of security and regulation.
- Adapting to Change: Both sectors must adapt to technological advancements and changing consumer expectations.
- Balancing Innovation and Security: Finding the right balance between fostering innovation and ensuring security and stability is crucial.
Security and regulation are critical aspects of the financial world, ensuring stability and protecting consumers. While cryptocurrency offers innovative solutions and challenges traditional systems, it faces significant security and regulatory hurdles. Traditional banking, with its well-established frameworks, provides a stable and secure environment but must continue to evolve to meet the changing needs of the global economy.
Impact on the Global Economy
The financial sector is a crucial component of the global economy, and both cryptocurrency and traditional banking play significant roles in shaping its future. This section explores their impacts, future trends, and potential shifts in power.
Cryptocurrency’s Changing Landscape
Cryptocurrency has introduced a paradigm shift, challenging traditional financial systems and offering innovative solutions.
- Financial Inclusion: Cryptocurrencies provide financial services to unbanked and underbanked populations, contributing to greater financial inclusion globally.
- Cross-Border Transactions: Cryptocurrencies facilitate faster and cheaper cross-border transactions, benefiting individuals and businesses alike.
- Decentralized Finance (DeFi): The rise of DeFi platforms allows users to lend, borrow, and earn interest on their cryptocurrency holdings, bypassing traditional financial intermediaries.
Traditional Banking’s Role
Traditional banking continues to be a pillar of stability and reliability in the financial world.
- Economic Stability: Banks play a crucial role in maintaining economic stability, providing loans to businesses, and supporting job creation.
- Monetary Policy: Traditional banks are integral to the implementation of monetary policy, influencing interest rates and money supply.
- Consumer Protection: Banks offer a range of consumer protection measures, ensuring the safety of deposits and providing recourse in case of disputes.
Future Trends and Potential Shifts
The financial sector is evolving rapidly, and future trends will likely shape the roles of both cryptocurrency and traditional banking.
- Blockchain Adoption: Traditional banks are exploring blockchain technology to improve efficiency, reduce costs, and enhance security.
- Central Bank Digital Currencies (CBDCs): Many countries are researching or developing their own digital currencies, which could bridge the gap between cryptocurrency and traditional banking.
- Sustainability: The environmental impact of cryptocurrency mining and the financial sector’s role in sustainable development are becoming increasingly important considerations.
Both cryptocurrency and traditional banking have profound impacts on the global economy, each with its unique advantages and challenges. Cryptocurrency offers innovative solutions and increased accessibility, while traditional banking provides stability and a comprehensive range of services. The future financial landscape will likely be shaped by their coexistence, with ongoing developments in technology and regulation playing a crucial role.
User Experience and Accessibility
The way users interact with financial systems is crucial, and both cryptocurrency and traditional banking offer unique experiences and levels of accessibility. This section delves into these aspects, highlighting the strengths and challenges of each.
User Experience in Cryptocurrency
Cryptocurrency provides a digital-first experience, catering to a tech-savvy audience.
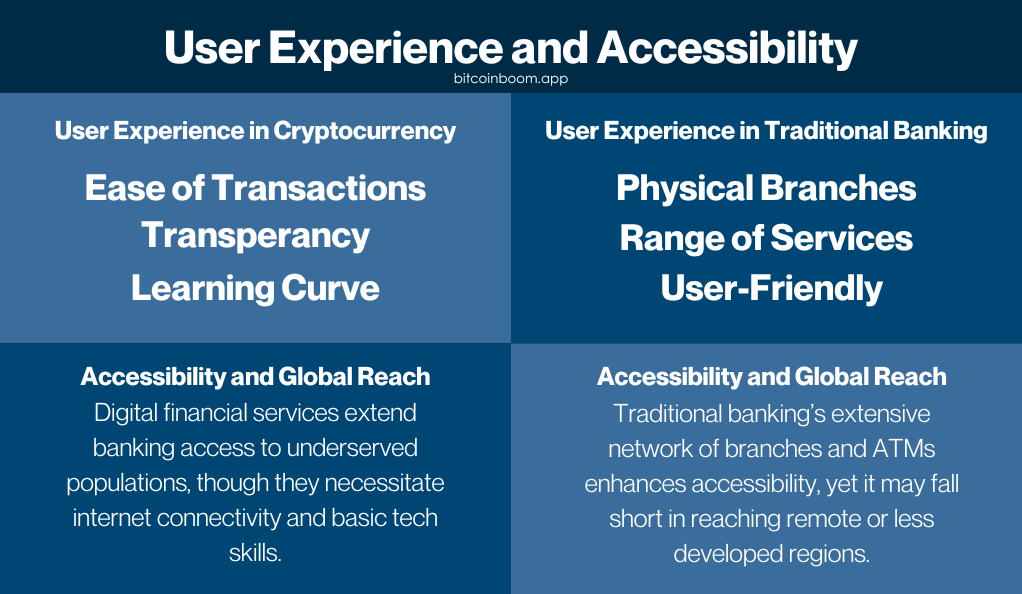
- Ease of Transactions: Users can perform transactions from anywhere at any time, providing convenience and flexibility.
- Transparency: All transactions are recorded on the blockchain, offering a high level of transparency.
- Learning Curve: The technology and concepts behind cryptocurrency can be complex, requiring users to educate themselves to use it effectively.
User Experience in Traditional Banking
Traditional banking offers a more established and familiar user experience.
- Physical Branches: The presence of physical branches allows for in-person assistance and a tangible connection to the bank.
- Range of Services: Banks offer a wide range of services, from loans and mortgages to investment advice, providing a comprehensive financial solution.
- User-Friendly: Banks have invested heavily in user-friendly online and mobile banking platforms, making it easier for users to manage their finances.
Accessibility and Global Reach
Both systems have their strengths and challenges when it comes to accessibility and reaching global audiences.
- Cryptocurrency: Provides financial services to those without access to traditional banking, but requires internet access and a certain level of technological literacy.
- Traditional Banking: Has a wide reach with physical branches and ATMs, but may still be inaccessible in remote or underdeveloped areas.
Bridging the Digital Divide
Efforts are being made to bridge the digital divide and ensure that financial services are accessible to all.
- Financial Education: Providing education on cryptocurrency and financial literacy can empower more people to access and benefit from these services.
- Technology Access: Initiatives to increase access to the internet and technology are crucial for the adoption of digital financial services.
User experience and accessibility are key factors in the adoption and effectiveness of financial systems. Cryptocurrency offers a digital, flexible solution, while traditional banking provides a familiar, comprehensive service. Bridging the digital divide and ensuring access to financial education and technology will be crucial in ensuring that both systems can serve the global population effectively.
Future Trends in Traditional Banking
Traditional banking is also undergoing transformation, adapting to new technologies and changing consumer expectations.
- Digital Transformation: Banks are investing heavily in digital technologies to improve efficiency, reduce costs, and enhance customer experience. This includes the adoption of blockchain, artificial intelligence, and machine learning.
- Personalized Services: Leveraging data analytics, banks are moving towards providing more personalized and tailored financial services to meet individual customer needs.
- Sustainable Banking: There is a growing trend towards sustainable and ethical banking practices, with banks playing a crucial role in financing renewable energy projects and promoting responsible lending.
- Collaboration with Fintech: Traditional banks are increasingly collaborating with fintech companies to innovate and offer new services, such as digital wallets, peer-to-peer lending, and robo-advisors.
Preparing for the Financial World of Tomorrow
The financial world is at a crossroads, with both cryptocurrency and traditional banking poised to play crucial roles in shaping the future.
- Education and Literacy: Enhancing financial literacy and understanding of new technologies is vital for individuals and businesses to navigate the evolving financial landscape.
- Security and Regulation: Ensuring robust security measures and clear regulatory frameworks will be crucial in building trust and stability in both cryptocurrency and traditional banking.
- Innovation and Adaptability: Embracing innovation and staying adaptable will be key for both sectors to thrive and continue serving the global population effectively.
The future of finance is bright, with immense potential for innovation, growth, and increased accessibility. Cryptocurrency and traditional banking each have unique strengths and challenges, and their coexistence and collaboration could lead to a more inclusive, efficient, and secure financial world. As we step into the future, the financial sector must remain vigilant, adaptable, and committed to serving the diverse needs of the global population.
Conclusion: Navigating the Financial Future
Cryptocurrency and traditional banking, each with their unique paradigms, have been meticulously dissected throughout this analysis, showcasing a financial world rich in diversity, challenges, and innovation. Cryptocurrency, with its decentralized nature, brings speed, accessibility, and a wave of innovation, yet grapples with issues of security, volatility, and regulatory ambiguity. Traditional banking, the long-standing pillar of financial stability, offers a comprehensive suite of services, customer support, and regulatory safety, but faces the imperative to evolve amidst rapid technological advancements and shifting consumer expectations. The comparative analysis underscores that these two financial systems, rather than being at odds, have the potential to coexist and complement each other, catering to diverse needs and preferences, and collectively enhancing the financial landscape.
Looking forward, the financial sector stands on the brink of transformative change, with both cryptocurrency and traditional banking poised to play pivotal roles. The future calls for a harmonious blend of innovation, stability, and consumer-centricity, fostering an inclusive, efficient, and secure financial ecosystem. Embracing change, building trust through transparency and robust security, and committing to financial inclusion will be key in navigating this journey. As we step into this future, armed with knowledge and a balanced perspective, we are better equipped to make informed decisions and contribute to shaping a prosperous and equitable financial world.